

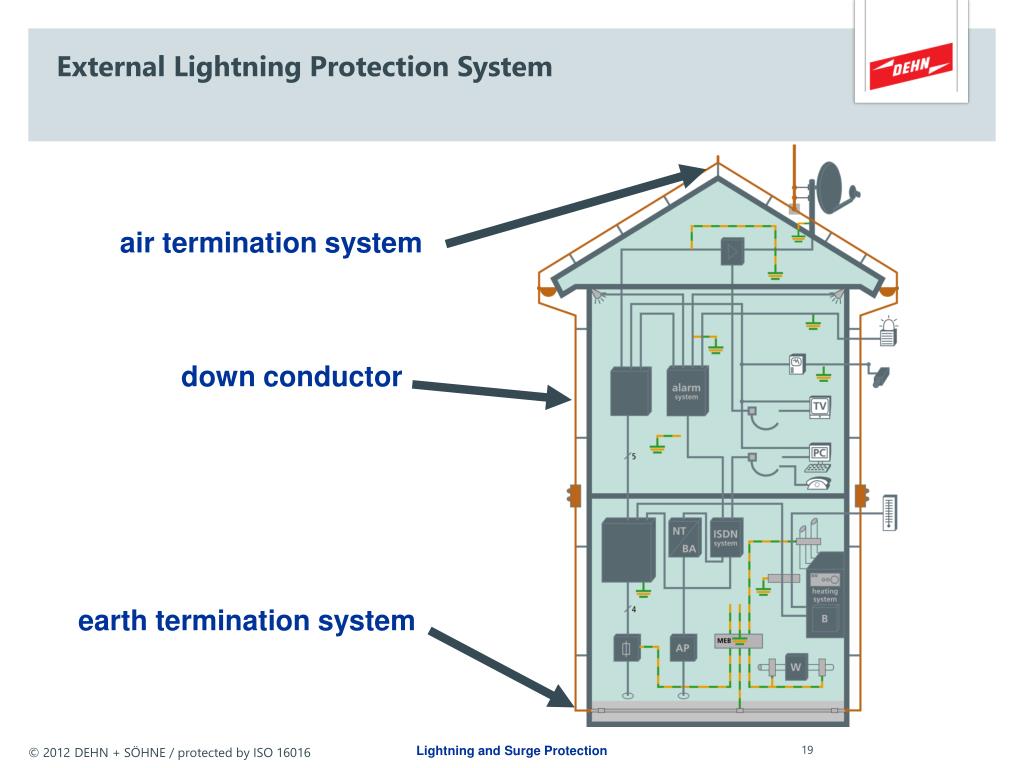
An internal LPS prevents dangerous sparking within the structure using either equipotential bonding or a separation distance between the external LPS components and other electrically conducting elements internal to the structure. An external LPS is intended to: (a) intercept a lightning flash to the structure, with an air-termination system (b) conduct the lightning current safely towards earth, using a down-conductor system (c) disperse the lightning current into the earth, using an earth-termination system. Lightning Protection System (LPS) usually consists of both external and internal lightning protection systems. Now, this acquired charge moves to the earth through the earthing system. Whenever a charged cloud passes by the building, the conductor gets charge opposite to that of the cloud through the process of induction. The lightning conductor works on the principle of induction. Lightning is a direct current and a typical lightning flash is about 300 million Volts and about 30,000 Amp. A lightning strike is essentially a cloud to ground lightning stroke where it strikes the ground. A single lightning flash can be made up of a number of strokes or pulses of current. Where the ice going down meets the water coming up, and then electrons are stripped off. In the meantime, downdrafts in the cloud push ice particles below from the top. Water droplets in the lower region of a cloud get attached to the updrafts and lifted to higher regions where the extreme cold atmosphere freezes them. Wind trapped inside the cloud is very turbulent. Lightning begins as static charges in a rain cloud. This happens millions of times per second and when this charge gets large enough a lightning strike occurs. The charge and lightning develops because of tiny collisions between ice particles within the cloud. Lightning is essentially a huge electric spark that occurs between the cloud and the ground. As lightning passes through the air it heats the air quickly. Lightning is a visible electrical discharge that occurs within a cloud, between two clouds, or between a cloud and the surface of the earth.
Lightning protection and earthing equipment are usually made up of earth rods either copper bonded, solid copper or stainless steel and also forming the earthing system are copper earth plates, copper lattice earth mats or 25 x 3mm copper earth tapes.
LIGHTNING PROTECTION SYSTEM TYPES CODE
IS 3043 (1987) is Code of practice for earthing. Grounding rods and wires are also used to create what is referred to as a common ground. This low-impedance path is installed to encourage the lightning to travel through it instead of through your expensive electronic equipment. The minimum depth at which the pipe must be buried in pipe earthing is 3.75 meter.Ī grounding system provides a low-impedance path to the ground. The depth at which the pipe must be buried depends on the moistures of the ground. The size of the pipe used for earthing is of diameter 40 mm and 2.5 meters in length for ordinary soil or greater length in case of dry and rocky soil. There are three types of earthing: Pipe earthing, Plate earthing, Strip earthing. Indirect grounding is performed by binding to the grounding system through impedance. Direct grounding is carried out by direct connection of the grounding system. Grounding can be performed directly or indirectly. The grounding includes measures for protecting the part of the circuit, which provides the desired function or the working feature of that circuit. Earthing reduces that voltage and prevents the emergence of conditions that are dangerous to the equipment, as well as the lives of people handling that equipment or which can be affected by the defect or by moving in the vicinity. Protective earthing includes measures for protecting the metal parts that neither belong to the circuits, nor are they in direct electrical contact with them, but in the event of a defect, a voltage can arise. It is located between the neutral of the equipment being used and the ground. Earthing is located under the earth pit, between the equipment body and underground. Grounding is primarily used for unbalancing when the electric system overloads. Also, the proper operation of over current protective devices is frequently dependent upon low impedance fault current paths.Įarthing is primarily used to avoid electric shocks. Equipment and building protection is provided by low impedance grounding and bonding between electrical services, protective devices, equipment and other conductive objects – so that faults or lightning currents do not result in hazardous voltages within the building.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
